-
Interaction
| AccNo. |
22454 |
Score |
0.86 |
| Name |
APTPV_HMGB1 |
Environment |
in vitro |
| Kd |
1.0 |
Organism |
N/A |
|
Peptide
| AccNo. |
22338 |
| Name |
APTPV |
| Organism |
N/A |
| Constraint |
none |
| Sequence |
APTPVKL
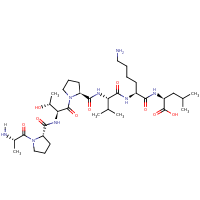
|
| Origin |
phage display |
| Form |
phage |
| Internalized |
no |
| Unnatural |
no |
| Imaging |
no |
| Is Motif |
no |
|
Interactor
| AccNo. |
22190 |
| Name |
HMGB1 |
| Description |
chromatin high mobility group protein 1, box A |
| Organism |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
| Type |
protein |
|
Experiment
| AccNo. |
22408 |
Classification incorrect?
Click the corresponding button to vote. Your vote
is used to improve the automatic classification.

|
| CA |
CVD |
DM |
APO |
ANG |
MI |
BD |
|
| 0.44 |
0.50 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Vote |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Yes |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No |
|
| Name |
PD_5 |
| Detection |
filamentous phage display, MI:0048 |
| Source |
PDF |
Text Id |
5 |
| Journal |
J Biol Chem. 2002 Mar 1;277(9):7021-8. Epub 2001 Dec 17. |
| Title |
HMGB1 interacts with many apparently unrelated proteins by recognizing short amino acid sequences. |
| Authors |
Dintilhac A, Bernués J |
| Text |
The chromatin high mobility group protein 1 (HMGB1) is a very abundant and conserved protein that is structured into two HMG box domains plus a highly acidic C-terminal domain. From the ability to bind DNA nonspecifically and to interact with various proteins, several functions in DNA-related processes have been assigned to HMGB1. Nevertheless, its functional role remains the subject of controversy. Using a phage display approach we have shown that HMGB1 can recognize several peptide motifs. A computer search of the protein data bases found peptide homologies with proteins already known to interact with HMGB1, like p53, and have allowed us to identify new potential candidates. Among them, transcriptional activators like the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K), repressors like methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2), and co-repressors like the retinoblastoma susceptibility protein (pRb) and Groucho-related gene proteins 1 (Grg1) and 5 (Grg5) can be found. A detailed analysis of the interaction of Grg1 with HMGB1 confirmed that the binding region contained the sequence homologous to one of the peptides identified. Our results have led us to propose that HMGB1 may play a central role in the stabilization and/or assembly of several multifunctional complexes through protein-protein interactions. |
| Mesh Terms |
Amino Acid Sequence; Amino Acids/chemistry; Animals; Binding Sites; Cattle; Chromosomal Proteins, Non-Histone; CpG Islands; DNA/chemistry; DNA-Binding Proteins/chemistry; Glutathione Transferase/metabolism; HMGB1 Protein/chemistry; HMGB1 Protein/genetics; Heterogeneous-Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein K; Heterogeneous-Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins; Methyl-CpG-Binding Protein 2; Models, Genetic; Molecular Sequence Data; Peptide Library; Peptides/chemistry; Plasmids/metabolism; Protein Binding; Protein Structure, Tertiary; Rats; Recombinant Fusion Proteins/metabolism; Recombinant Proteins/metabolism; Repressor Proteins/chemistry; Retinoblastoma Protein/chemistry; Ribonucleoproteins/chemistry; Sequence Homology, Amino Acid; Trans-Activation (Genetics); Transcription, Genetic; Tumor Suppressor Protein p53/chemistry |
References
|