-
Interaction
| AccNo. |
22428 |
Score |
0.86 |
| Name |
CEHFF_ather |
Environment |
in vivo |
| Kd |
1.0 |
Organism |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
|
Peptide
| AccNo. |
22312 |
| Name |
CEHFF |
| Organism |
N/A |
| Constraint |
disulfide |
| Sequence |
CEHFFSRSC
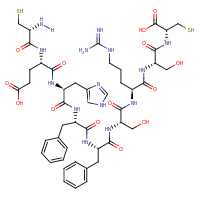
|
| Origin |
phage display |
| Form |
phage |
| Internalized |
no |
| Unnatural |
no |
| Imaging |
no |
| Is Motif |
no |
|
Interactor
| AccNo. |
22156 |
| Name |
ather |
| Description |
atherosclerotic lesions from aorta of ApoE knockout mice |
| Organism |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
| Type |
tissue |
|
Experiment
| AccNo. |
22375 |
Classification incorrect?
Click the corresponding button to vote. Your vote
is used to improve the automatic classification.

|
| CA |
CVD |
DM |
APO |
ANG |
MI |
BD |
|
| 0.50 |
0.52 |
0.52 |
0.50 |
0.52 |
0.49 |
0.49 |
Vote |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Yes |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No |
|
| Name |
PD_4 |
| Detection |
filamentous phage display, MI:0048 |
| Source |
PDF |
Text Id |
4 |
| Journal |
Am J Pathol. 2003 Nov;163(5):1859-71. |
| Title |
In vivo interrogation of the molecular display of atherosclerotic lesion surfaces. |
| Authors |
Liu C, Bhattacharjee G, Boisvert W, Dilley R, Edgington T |
| Text |
The endothelial surface of atherosclerotic lesions of ApoE knockout mice was interrogated by in vivo biopanning with a phage-displayed constrained peptidyl library. Through repeated biopanning, 103 peptidyl sequences were identified, many are homologous to known proteins. The sequence CAPGPSKSC contains motifs that are shared by 9.7% of selected peptides. On phage or as a synthetic peptide, this constrained peptide selectively bound to atherosclerotic lesion surfaces of ApoE knockout mice in vivo and of human atherosclerotic lesions ex vivo. A cell-surface protein of approximately 82 kd recognized by this peptide was affinity-purified and determined by mass spectrometry analysis as glucose-regulated protein 78 (Grp78), indicating the surprising presence of this endoplasmic reticulum chaperone on the endothelial cell surface of atherosclerotic lesions. Peptides that mimicked binding functions of their homologues were demonstrated with three peptides homologous to tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2), ie, CNHRYMQMC, CNQRHQMSC, and CNNRSDGMC. Phage carrying CNHRYMQMC bound to atherosclerotic lesion endothelium of ApoE knockout mice in vivo. The three peptides bound to endothelial cells in a dose-dependent manner and were inhibited by TIMP-2 protein. These peptides provide a set of probes to interrogate the cell surface repertoire associated with atherogenesis and thrombotic complications. |
| Mesh Terms |
Amino Acid Sequence; Animals; Apolipoproteins E/genetics; Arteriosclerosis/metabolism; Arteriosclerosis/pathology; Blotting, Western; Carrier Proteins/analysis; Carrier Proteins/metabolism; Chromatography; Endothelium, Vascular/chemistry; Endothelium, Vascular/metabolism; Endothelium, Vascular/pathology; Flow Cytometry; Heat-Shock Proteins; Humans; Immunohistochemistry; Mass Spectrometry; Mice; Mice, Knockout; Molecular Chaperones/analysis; Molecular Chaperones/metabolism; Peptide Library; Peptides/metabolism; Precipitin Tests; Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-2/analysis; Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-2/metabolism |
References
|